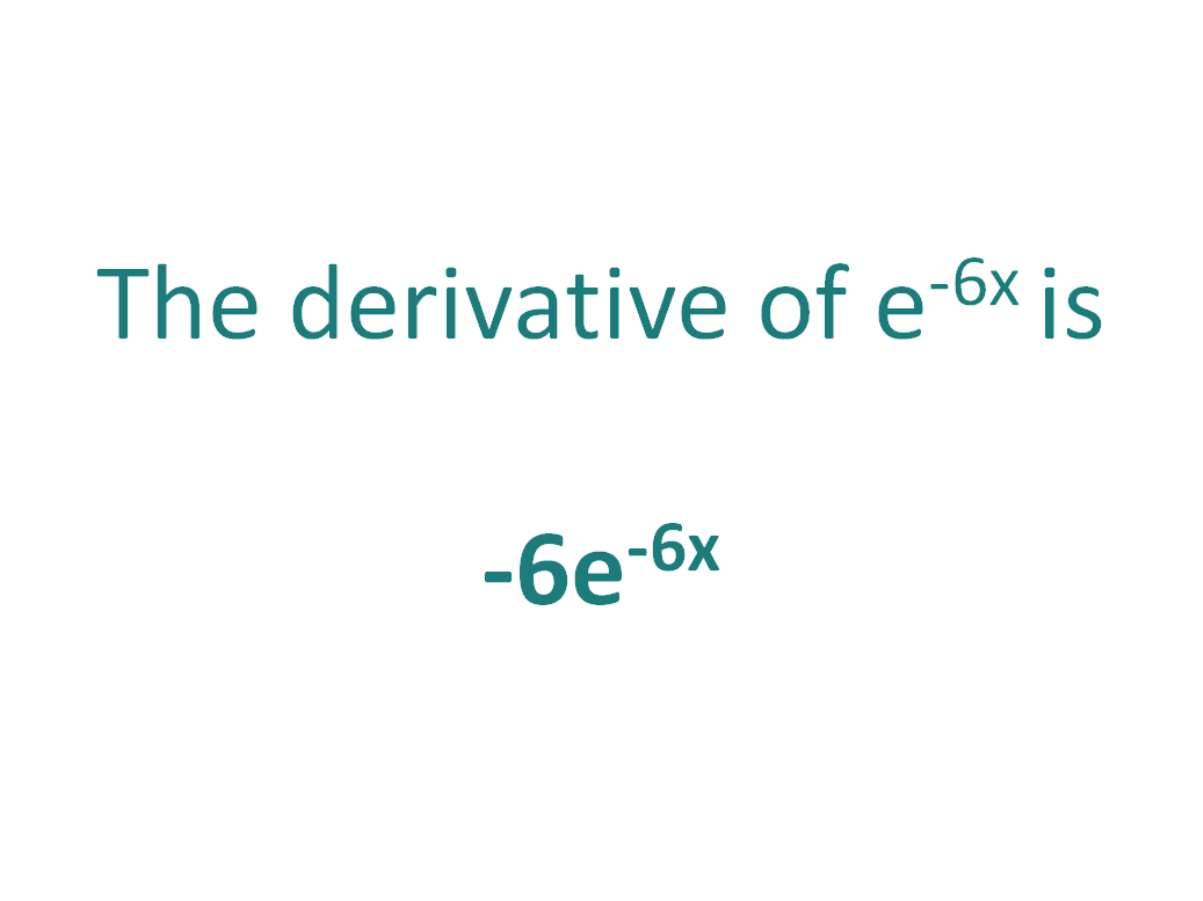The derivative of e^-6x is -6e^-6x
How to calculate the derivative of e^-6x
The chain rule is useful for finding the derivative of a function which could have been differentiated had it been in x, but it is in the form of another expression which could also be differentiated if it stood on its own.
In this case:
- We know how to differentiate ex (the answer is ex)
- We know how to differentiate -6x (the answer is -6)
Because e^-6x is a function which is a combination of ex and -6x, it means we can perform the differentiation of e to the -6x by making use of the chain rule.
Using the chain rule to find the derivative of e^-6x
Although the function e-6x contains no parenthesis, we can still view it as a composite function (a function of a function).
If we add parenthesis around the exponent, we get e(-6x).
Now the function is in the form of the standard exponential function ex, except it does not have x as an exponent, instead the exponent is another function of x (-6x).
Let’s call the function in the exponent g(x), which means:
g(x) = -6x
From this it follows that:
e-6x = eg(x)
Let’s set f(x) = ex.
Then, because g(x) = -6x, the function e-6x can be written as a composite function of f(x) and g(x).
f(x) = ex
f(g(x)) = eg(x) (but g(x) = -6x)
Therefore, f(g(x)) = e-6x
Let’s define this composite function as F(x):
F(x) = f(g(x)) = e-6x
We can now find the derivative of F(x) = e^-6x, F'(x), by making use of the chain rule.
The Chain Rule:
For two differentiable functions f(x) and g(x)
If F(x) = f(g(x))
Then the derivative of F(x) is F'(x) = f’(g(x)).g’(x)
Now we can just plug f(x) and g(x) into the chain rule to find the derivative of e to the -6x.
How to find the derivative of e^-6x using the Chain Rule:
| F'(x) | = f'(g(x)).g'(x) | Chain Rule Definition |
| = f'(g(x))(-6) | g(x) = -6x ⇒ g'(x) = -6 | |
| = (e^-6x)(-6) | f(g(x)) = e^-6x ⇒ f'(g(x)) = e^-6x | |
| = -6e^(-6x) |
Using the chain rule, the derivative of e^-6x is -6e^-6x
Finally, just a note on syntax and notation: the exponential function e^-6x is sometimes written in the forms shown below (the derivative of each is as per the calculations above). Just be aware that not all of the forms below are mathematically correct.
| e-6x | ► Derivative of e-6x = -6e-6x |
| e^(-6x) | ► Derivative of e^(-6x) = -6e-6x |
| e -6x | ► Derivative of e -6x = -6e-6x |
| e -6 x | ► Derivative of e -6 x = -6e-6x |
| e to the -6x | ► Derivative of e to the -6x = -6e-6x |
Top Tip
It’s possible to generalize the derivative of expressions in the form e^ax (where a is a constant value):
The derivative of eax = aeax
(Add the constant a to the front of the expression and keep the exponential part the same)
The Second Derivative of e^-6x
To calculate the second derivative of a function, you just differentiate the first derivative.
From above, we found that the first derivative of e^-6x = -6e^(-6x). So to find the second derivative of e^-6x, we just need to differentiate -6e-6x
We can use the chain rule to calculate the derivative of -6e-6x and get an answer of 36e-6x.
► The second derivative of e^-6x = 36e^(-6x)