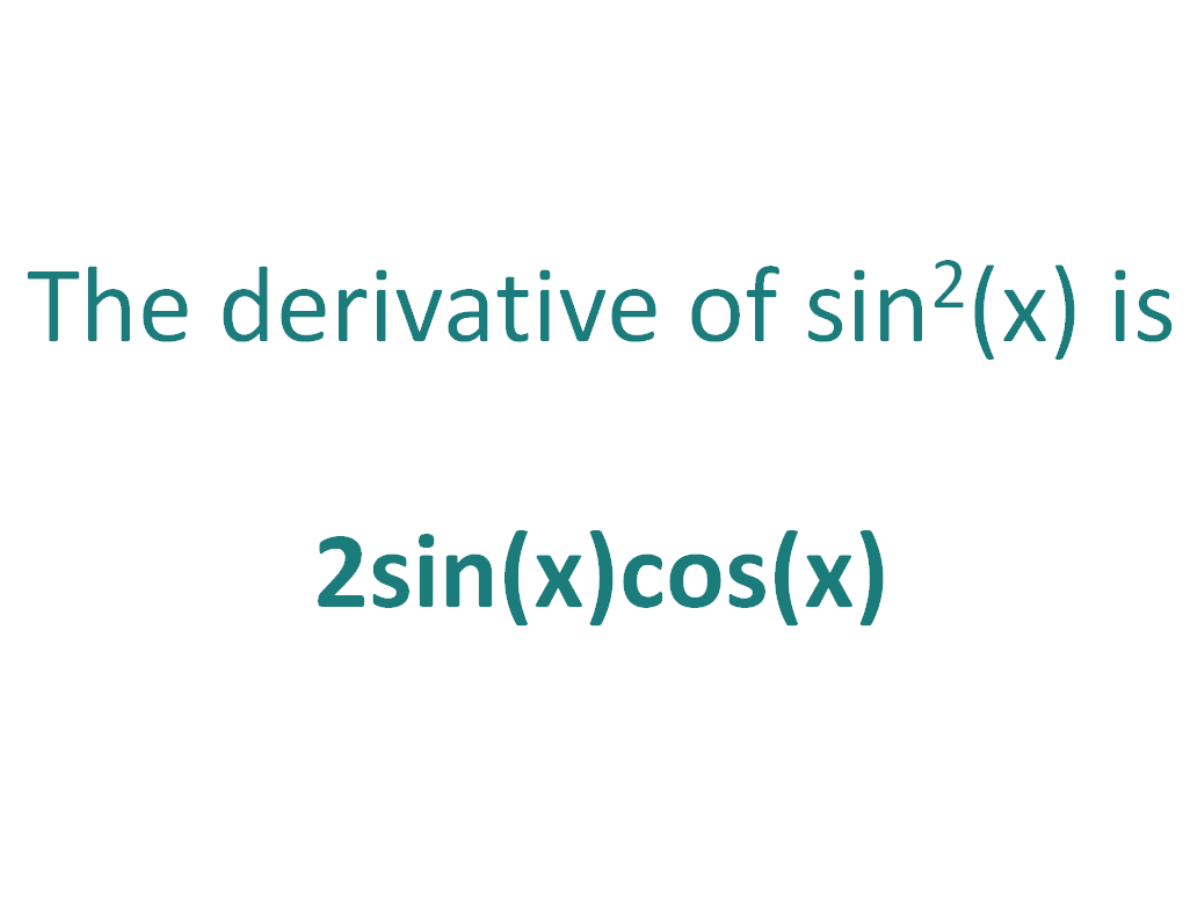The derivative of sin^2x is 2sin(x)cos(x)
How to calculate the derivative of sin^2x
Note that in this post we will be looking at differentiating sin2(x) which is not the same as differentiating sin(2x). Here is our post dealing with how to differentiate sin(2x).
There are two methods that can be used for calculating the derivative of sin^2x.
The first method is by using the product rule for derivatives (since sin2(x) can be written as sin(x).sin(x)).
The second method is by using the chain rule for differentiation.
Finding the derivative of sin^2x using the product rule
The product rule for differentiation states that the derivative of f(x).g(x) is f’(x)g(x) + f(x).g’(x)
The Product Rule:
For two differentiable functions f(x) and g(x)
If F(x) = f(x).g(x)
Then the derivative of F(x) is F'(x) = f’(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)
First, let F(x) = sin2(x)
Then remember that sin2(x) is equal to sin(x).sin(x)
So F(x) = sin(x)sin(x)
By setting f(x) and g(x) as sin(x) means that F(x) = f(x).g(x) and we can apply the product rule to find F'(x)
| F'(x) | = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x) | Product Rule Definition |
| = f'(x)sin(x) + sin(x)g'(x) | f(x) = g(x) = sin(x) | |
| = cos(x)sin(x) + sin(x)cos(x) | f'(x) = g(‘x) = cos(x) | |
| = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
Using the product rule, the derivative of sin^2x is 2sin(x)cos(x)
Finding the derivative of sin^2x using the chain rule
The chain rule is useful for finding the derivative of a function which could have been differentiated had it been in x, but it is in the form of another expression which could also be differentiated if it stood on its own.
In this case:
- We know how to differentiate sin(x) (the answer is cos(x))
- We know how to differentiate x2 (the answer is 2x)
This means the chain rule will allow us to perform the differentiation of the expression sin^2x.
Using the chain rule to find the derivative of sin^2x
Although the expression sin2x contains no parenthesis, we can still view it as a composite function (a function of a function).
We can write sin2x as (sin(x))2.
Now the function is in the form of x2, except it does not have x as the base, instead it has another function of x (sin(x)) as the base.
Let’s call the function of the base g(x), which means:
g(x) = sin(x)
From this it follows that:
sin(x)2 = g(x)2
So if the function f(x) = x2 and the function g(x) = sin(x), then the function (sin(x))2 can be written as a composite function.
f(x) = x2
f(g(x)) = g(x)2 (but g(x) = sin(x))
f(g(x)) = (sin(x))2
Let’s define this composite function as F(x):
F(x) = f(g(x)) = (sin(x))2
We can find the derivative of sin^2x (F'(x)) by making use of the chain rule.
The Chain Rule:
For two differentiable functions f(x) and g(x)
If F(x) = f(g(x))
Then the derivative of F(x) is F'(x) = f’(g(x)).g’(x)
Now we can just plug f(x) and g(x) into the chain rule.
How to find the derivative of sin^2x using the Chain Rule:
| F'(x) | = f'(g(x)).g'(x) | Chain Rule Definition |
| = f'(g(x))(cos(x)) | g(x) = sin(x) ⇒ g'(x) = cos(x) | |
| = (2sin(x)).(cos(x)) | f(g(x)) = (sin(x))2 ⇒ f'(g(x)) = 2sin(x) | |
| = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
Using the chain rule, the derivative of sin^2x is 2sin(x)cos(x)
(Note – using the trigonometric identity 2cos(x)sin(x) = sin(2x), the derivative of sin^2x can also be written as sin(2x))
Finally, just a note on syntax and notation: sin^2x is sometimes written in the forms below (with the derivative as per the calculations above). Just be aware that not all of the forms below are mathematically correct.
| sin2x | ► Derivative of sin2x = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
| sin^2(x) | ► Derivative of sin^2(x) = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
| sin 2 x | ► Derivative of sin 2 x = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
| (sinx)^2 | ► Derivative of (sinx)^2 = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
| sin squared x | ► Derivative of sin squared x = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
| sinx2 | ► Derivative of sinx2 = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
| sin^2 | ► Derivative of sin^2 = 2sin(x)cos(x) |
The Second Derivative Of sin^2x
To calculate the second derivative of a function, you just differentiate the first derivative.
From above, we found that the first derivative of sin^2x = 2sin(x)cos(x). So to find the second derivative of sin^2x, we just need to differentiate 2sin(x)cos(x)
We can use the product rule to find the derivative of 2sin(x)cos(x).
We can set f(x) = 2sin(x) and g(x) = cos(x) and apply the product rule to find the derivative of f(x).g(x) = 2sin(x)cos(x)
The product rules says that the derivative of f(x).g(x) is equal to f’(x)g(x) + f(x)g’(x).
2cos(x)cos(x) + 2sin(x)(-sin(x))
= 2cos2(x) – 2sin2(x)
= 2(cos2(x) – sin2(x))
Using the trigonometric double angle identity cos(2x) = cos2(x) – sin2(x), we can rewrite this as
= 2cos(2x)
► The second derivative of sin^2x is 2cos(2x)
Interestingly, the second derivative of sin2x is equal to the first derivative of sin(2x).